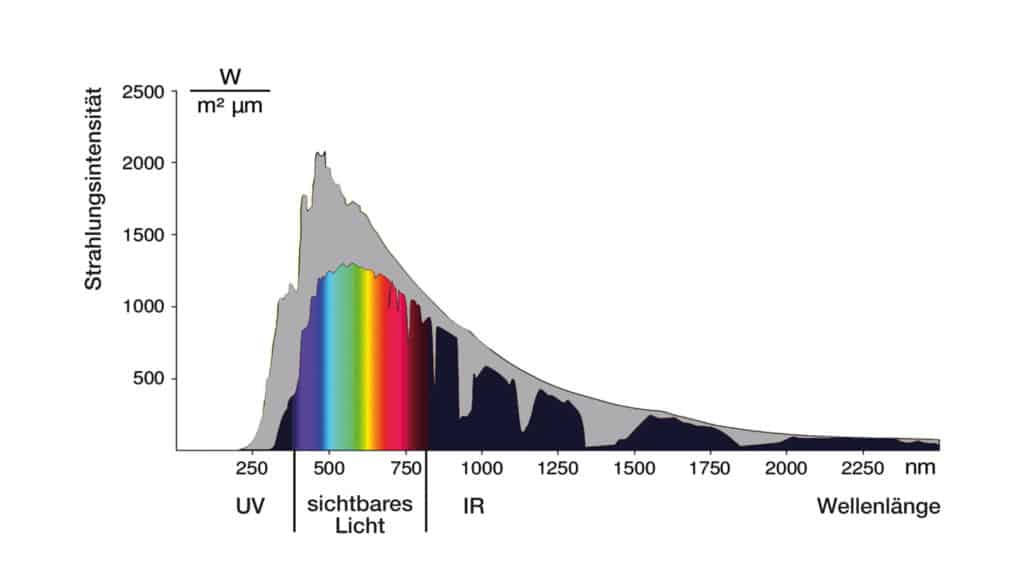
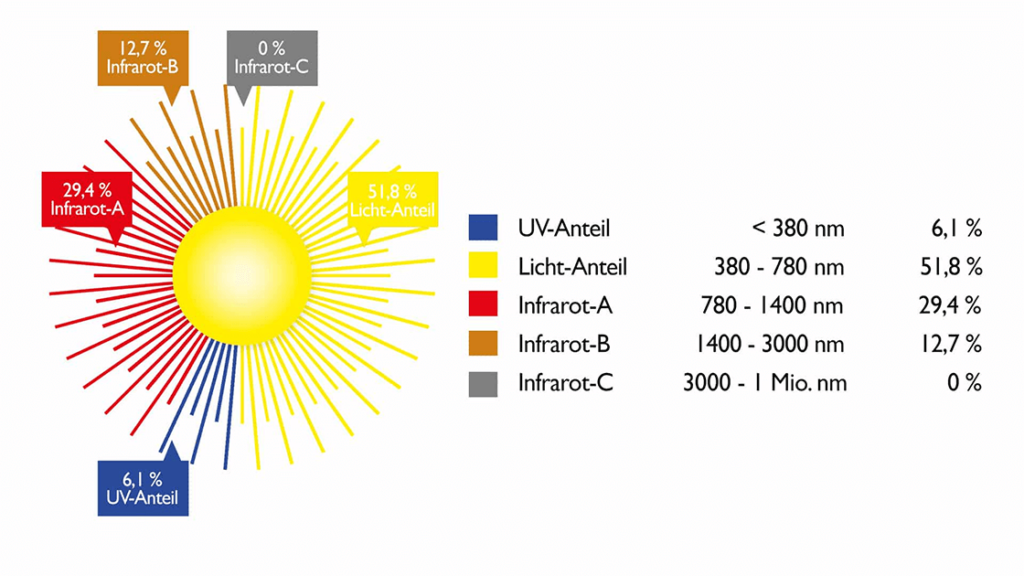
According to the findings of the Association for Radiation Protection, infrared rays with a wavelength between 780 and 10,000nm can significantly damage the eye. In contrast to UV rays, the energy of the IR rays is not sufficient to cause photochemical editing, but the rays lead to a significant warming of the inside of the eye.
The key question for assessing the damage is: What actually arrives where?
The IR-A part, which is dominant in sunlight, penetrates in the range up to 1,400nm with a significant part even as far as the retina. This is simply a result of the general rule: the shorter the IR radiation, the greater the penetration depth. This particularly affects the choroid (choroid), which can be damaged by IR-A. This can lead to local tissue defects in the retina (retina). Only a small portion of radiation that is longer than 2000 nm comes through the cornea. The anterior chamber of the eye absorbs all radiation above 2000nm. All wavelengths greater than 1400nm are filtered out by the lens and glass body.
Radiation in the wavelength range from 400 nm to 1400 nm can essentially fall on the retina. The energy of the infrared radiation absorbed by the eye leads to warming (Von and Norren 2004, Brose et al. 2005). The exact mechanism of action that leads to clouding of the lens of the eye (cataract) in the event of long-term exposure to IR radiation is still controversial (Brose et al. 2005). It is also difficult to distinguish it from the fundamentally multifactorial age-dependent cataract development with a large number of biochemical changes – in particular changes in the composition of lens proteins with increasing aggregations of water-insoluble high-molecular proteins – and cellular changes that are genetically modified and are expanded and reinforced by environmental factors (Truscott and Uhu , Michael and Born 20122). * It is not for nothing, however, that certain cataract diseases are referred to as fire star or glass blower star, so that an influence of infrared radiation on such training, although difficult to detect due to the very long development and thus a difficult test setup, but as very likely to apply.
* Guideline of the German Society for Occupational and Environmental Medicine. Work under the influence of infrared radiation (heat radiation). Hazards and damage to eyes and skin (AWMF register No. 002/010 class: S1 02/2012).